Are you tired of the endless cycle of diets that promise the world but deliver fleeting results? Perhaps you’ve heard whispers about intermittent fasting for weight loss, and the idea of “when” you eat, rather than just “what” you eat, has piqued your interest. It’s a powerful approach, but let’s be honest: the internet is flooded with generic advice. You might feel overwhelmed by the rigid 16:8 protocol or wonder if it’s just another fleeting trend. The truth is, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to an intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss. Your unique lifestyle, body, and goals demand a personalized strategy.
This isn’t about pushing you into a restrictive box. Instead, we’ll dive deep into the science and practicalities, helping you understand how different fasting schedules impact your body’s fat metabolism and overall well-being. We’ll explore why customization is key, moving beyond the typical guidelines to help you discover an intermittent fasting plan that feels effortless, sustainable, and truly effective for shedding pounds. Get ready to transform your relationship with food and unlock a healthier, leaner you – on your terms.
Understanding the Core Mechanism: Why Intermittent Fasting Works for Weight Loss
At its heart, intermittent fasting for weight loss isn’t about starvation; it’s about optimizing your body’s natural fat-burning machinery. When you extend periods without food, several profound physiological shifts occur that directly contribute to shedding pounds and boosting metabolism. The primary driver is a reduction in overall calorie intake, often without consciously counting calories. By simply shortening your eating window, you naturally consume fewer meals and, for most people, fewer total calories throughout the day. This caloric deficit is fundamental to any weight loss journey.
Beyond calorie reduction, the magic of intermittent fasting lies in its impact on hormones, particularly insulin. When you eat, your body releases insulin to shuttle glucose from your bloodstream into your cells for energy. High insulin levels signal to your body to store fat. During a fasted state, insulin levels drop significantly. This low insulin environment signals to your body to switch from burning glucose for energy to tapping into its stored fat reserves, a process known as fat metabolism. This means your body becomes more efficient at burning fat for fuel, including stubborn belly fat.
Furthermore, intermittent fasting promotes a process called autophagy, where your cells clean out damaged components and regenerate newer, healthier ones. While not directly a weight loss mechanism, this cellular repair contributes to overall metabolic health, which indirectly supports sustainable weight management. It’s a holistic approach that goes beyond mere calorie restriction, leveraging your body’s inherent wisdom to drop weight and transform your body composition. This shift in metabolic flexibility is crucial for long-term success, helping your body become a more efficient fat-burning machine.
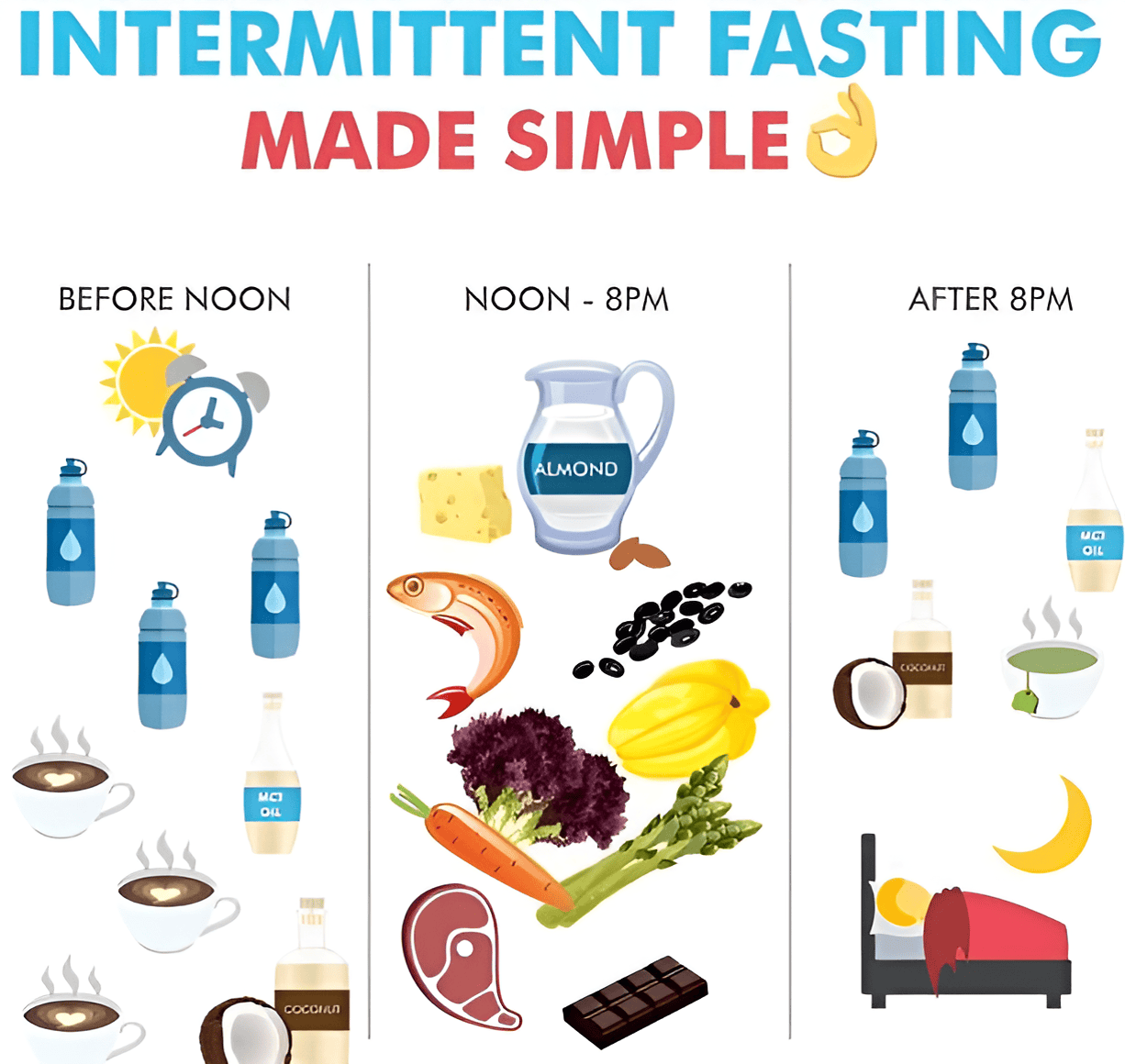
Different Intermittent Fasting Schedules: Finding Your Fit
The beauty of intermittent fasting for weight loss lies in its flexibility. There’s a spectrum of schedules, and understanding their nuances is key to finding one that integrates seamlessly into your life and helps you achieve your weight reduction goals. No single intermittent fasting plan is universally superior; the “best” one is the one you can consistently stick with.
The 16:8 Method: The Popular Starting Point
This is arguably the most common and beginner-friendly intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss. You fast for 16 hours and have an 8-hour eating window.
-
How it works: Typically, this involves skipping breakfast. For example, you might eat your first meal around 12 PM and finish your last meal by 8 PM. During the 16-hour fast, you can drink water, black coffee, and plain tea.
-
Why it’s effective: The 16-hour fast is long enough for insulin levels to drop and fat burning to begin, but short enough that it’s generally manageable for most people to avoid extreme hunger. It makes it easier to naturally reduce calorie intake without feeling deprived.
-
Considerations: This method fits well with social schedules as most social eating happens in the evening. It’s an excellent intermittent fasting meal plan for beginners due to its relative ease of adoption.
The 5:2 Diet: Flexible Fast Days
This schedule involves eating normally five days a week and restricting calorie intake to 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days.
-
How it works: On your “fasting” days, you’d consume very few calories, typically spread across one or two small meals. The other five days are regular eating days, focusing on healthy, balanced nutrition.
-
Why it’s effective: The concentrated calorie restriction on fast days can create a significant weekly calorie deficit, leading to effective weight loss. It allows for more flexibility on “normal” days, which some find easier to sustain than daily time restrictions.
-
Considerations: Some individuals might find the very low-calorie days challenging due to increased hunger or fatigue. Planning your fast days to avoid highly demanding activities is often recommended.
Alternate-Day Fasting (ADF): More Intense, Potentially Faster Results
ADF involves alternating between days of normal eating and days of complete or near-complete fasting (0-500 calories).
-
How it works: One day you eat freely, the next you significantly restrict calories or fast entirely. This pattern continues.
-
Why it’s effective: The larger and more frequent calorie deficits can lead to quicker weight loss for some individuals. It can also significantly boost fat metabolism.
-
Considerations: This is a more challenging protocol and often better suited for experienced fasters or those with specific weight loss goals who have discussed it with a healthcare professional. It can be difficult to sustain long-term for many people.
The “Eat-Stop-Eat” Method: Weekly Extended Fasts
This involves one or two 24-hour fasts per week.
-
How it works: You might finish dinner on Monday and not eat again until dinner on Tuesday, completing a full 24-hour fast.
-
Why it’s effective: The extended fast pushes the body further into a fat-burning state and can create a substantial calorie deficit. It can also be psychologically beneficial, proving to yourself you can go longer without food.
-
Considerations: This method requires more discipline and might be best introduced gradually after practicing shorter fasts. Managing hunger and energy levels during the 24-hour fast is crucial.
The key takeaway is to experiment safely and listen to your body. Starting with a less restrictive schedule, like 16:8, and gradually adjusting as you become more comfortable is a smart approach.
Tailoring Your Fasting Schedule for Optimal Weight Loss
While the general principles of intermittent fasting for weight loss apply to everyone, individual responses can vary significantly. What works wonders for one person might be challenging or less effective for another. Recognizing and adapting to these individual differences is paramount for long-term success and to truly slim down. This isn’t just about choosing an intermittent fasting plan; it’s about making it your plan.
Gender-Specific Considerations
-
For Women: Women’s hormonal systems are more sensitive to caloric restriction and stress. Aggressive or prolonged fasting can sometimes impact menstrual cycles, fertility, and thyroid function. Shorter fasting windows (e.g., 14:10 or 16:8) are often recommended as a starting point. It might be beneficial to cycle fasting days, perhaps taking a break around menstruation or during ovulation, to support hormonal balance. Listening to your body’s signals of fatigue or increased stress is critical.
-
For Men: Men generally tolerate longer fasting windows more readily than women, with fewer reported hormonal disruptions. Protocols like 16:8 or even 18:6 can be highly effective for men aiming to burn fat and build muscle. However, men still need to be mindful of overall nutritional intake during eating windows to ensure they’re meeting their macro and micronutrient needs.
Age and Lifestyle Factors
-
Intermittent Fasting by Age: As we age, metabolic rates can slow, and muscle mass tends to decrease. Intermittent fasting can still be highly beneficial for older adults to combat these changes and achieve weight management. However, starting with shorter fasts and ensuring adequate protein intake during eating windows becomes even more crucial to preserve muscle mass. Younger, highly active individuals might need to be more strategic with their fasting windows to fuel workouts and recovery.
-
Activity Levels: If you have an intense exercise routine, timing your eating window around your workouts can be vital. Some find exercising in a fasted state boosts fat burning, while others prefer to eat before or immediately after to optimize performance and recovery. High-intensity training might require a slightly shorter fasting window or a more strategic meal timing to ensure adequate fuel.
-
Stress and Sleep: Chronic stress and poor sleep can undermine any weight loss effort, including intermittent fasting. High stress hormones can counteract the benefits of fasting. Ensuring you manage stress and prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep can significantly enhance your body’s ability to respond positively to an intermittent fasting schedule, helping you to truly drop weight effectively.
Ultimately, pay close attention to how your body feels. Are you energized or drained? Is your sleep improving or worsening? Are you experiencing excessive hunger or irritability? These are all important cues that indicate whether your chosen intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss is truly working for you. Don’t be afraid to adjust and iterate until you find your sweet spot.

Beyond the Fast: Strategic Eating for Enhanced Weight Loss
Choosing the right intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss is only half the battle. What you eat during your eating window, and how you break your fast, are equally, if not more, important. This is where many people stumble, negating the benefits of their fasting efforts. The goal isn’t just to eat less, but to eat better to optimize your body for burning fat and promoting overall health.
Prioritizing Nutrient-Dense Foods
Your eating window isn’t a free-for-all. To truly shed pounds and support your body, focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
-
Protein Power: Prioritize lean proteins like chicken, fish, eggs, and legumes. Protein is incredibly satiating, helps preserve muscle mass (which is crucial for a healthy metabolism), and requires more energy to digest. Aim for adequate protein at each meal to feel fuller for longer.
-
Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Fats provide sustained energy, help with nutrient absorption, and contribute to satiety. Don’t fear healthy fats; they are essential for hormone production and overall well-being.
-
Fiber-Rich Carbohydrates: Opt for complex carbohydrates from vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. These provide sustained energy, essential vitamins and minerals, and dietary fiber, which aids digestion and helps stabilize blood sugar, preventing cravings and supporting gut health. Avoid refined sugars and processed carbs, which can cause rapid insulin spikes.
Breaking Your Fast Mindfully
The first meal after your fast is crucial. Your digestive system has been resting, so introducing food gently is key to avoid discomfort and optimize nutrient absorption.
-
Start Light: For longer fasts (e.g., 24 hours), consider starting with easily digestible foods like bone broth, a small salad with healthy fats, or a light protein shake.
-
Balanced Macros: For shorter fasts (e.g., 16:8), your first meal should ideally be balanced, containing a good mix of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. This helps stabilize blood sugar and keeps you feeling full.
-
Hydration is Key: Continue to hydrate throughout your eating window. Water, herbal teas, and electrolyte-rich drinks are excellent choices.
Remember, the goal is to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to thrive, repair, and efficiently burn fat. A healthy diet combined with your intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss is the winning formula for a genuine transformation.
Overcoming Common Challenges and Staying Consistent
Embarking on an intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss isn’t always smooth sailing. Like any significant lifestyle change, you’re likely to encounter hurdles. The good news is that most challenges are temporary and can be overcome with a little planning and persistence. Consistency is the real secret to seeing sustainable results and truly achieving your weight loss goals.
Managing Hunger Pangs
-
Hydrate Strategically: Often, thirst is mistaken for hunger. During your fasting window, drink plenty of water, black coffee, or plain tea. Sometimes, a glass of water with a pinch of pink Himalayan salt can curb cravings.
-
Stay Busy and Distracted: Engage in activities that take your mind off food. This could be work, a hobby, or light exercise.
-
Electrolytes: If you’re feeling lightheaded or weak, it might be an electrolyte imbalance. Consider adding some electrolytes (sugar-free) to your water, especially during longer fasts.
-
Gradual Adaptation: Don’t jump into extreme fasts immediately. Start with shorter windows, like 12:12 or 14:10, and gradually extend your fasting period as your body adapts. This helps manage hunger more effectively.
Dealing with Low Energy or “Fasting Flu”
-
Electrolytes (Again!): This is often the culprit behind “fasting flu” symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and brain fog. Ensure adequate sodium, potassium, and magnesium intake.
-
Proper Nutrition in Eating Window: Ensure your meals during the eating window are nutrient-dense and provide sufficient calories. Depriving your body during the eating period can exacerbate low energy during the fast.
-
Listen to Your Body: If you feel genuinely unwell, break your fast. Intermittent fasting should make you feel better, not worse. Push through minor discomfort, but prioritize your well-being.
Social Situations and Peer Pressure
-
Communicate: Let friends and family know about your intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss. Explain your reasons without being preachy.
-
Plan Ahead: If you have a dinner party, consider adjusting your eating window for that day, or strategically eat beforehand. Intermittent fasting is flexible; it doesn’t have to be rigid to be effective.
-
Focus on the “Why”: Remind yourself of your reasons for adopting this lifestyle. Your commitment to a healthier you and to burn fat should be your primary motivator.
By anticipating these challenges and having strategies in place, you can build resilience and ensure your intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss becomes a sustainable and enjoyable part of your life. Remember, progress over perfection.
Beyond Weight: The Wider Benefits of Your Intermittent Fasting Schedule
While the primary goal of adopting an intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss is often to drop weight, the benefits extend far beyond the scale. This dietary pattern can usher in a cascade of positive changes that enhance overall health and well-being, providing compelling reasons to continue even after you’ve reached your desired weight. It’s not just about weight reduction; it’s about a holistic transformation.
Metabolic Health Improvement
-
Insulin Sensitivity: Intermittent fasting significantly improves insulin sensitivity. When your cells become more responsive to insulin, your body doesn’t need to produce as much of it. Lower insulin levels are crucial for effective fat metabolism, reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, and overall metabolic health. This is a cornerstone benefit, especially for those looking to prevent or manage metabolic syndrome.
-
Blood Sugar Regulation: By giving your digestive system a break, intermittent fasting helps stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day, preventing the spikes and crashes that often lead to cravings and energy dips. This stable blood sugar contributes to consistent energy and can help with craving management.
-
Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is linked to various diseases, including obesity and heart disease. Studies suggest that intermittent fasting can reduce markers of inflammation in the body, contributing to a healthier state and potentially preventing chronic ailments.
Brain Health and Cognitive Function
-
Neuroprotection: Research indicates that fasting can promote brain health by increasing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and survival of nerve cells. This can enhance cognitive function, memory, and may even protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Mental Clarity: Many people report increased mental clarity, focus, and improved productivity during their fasting windows. This is often attributed to the stable blood sugar levels and the body’s shift to burning ketones for fuel, which can be a more efficient energy source for the brain.
Cellular Repair and Longevity
-
Autophagy: As mentioned earlier, intermittent fasting triggers autophagy, the body’s cellular “housekeeping” process. This not only helps clean out damaged cells but is also linked to anti-aging benefits and disease prevention. By promoting cellular renewal, your body maintains a healthier and more youthful state.
-
Growth Hormone Increase: Fasting can naturally increase human growth hormone (HGH) levels, which play a vital role in fat loss, muscle gain, and overall vitality. Higher HGH levels can help in preserving lean muscle mass while you’re trying to burn fat.
These additional benefits underscore why an intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss is more than just a diet; it’s a powerful tool for optimizing your health on multiple fronts. It’s about building a foundation for a healthier, more vibrant life, far beyond just seeing the numbers on the scale drop.

When to Seek Professional Guidance for Your Intermittent Fasting Schedule
While intermittent fasting for weight loss can be incredibly beneficial for many, it’s not suitable for everyone. Knowing when to seek professional guidance is crucial for your safety and to ensure you’re adopting a sustainable and healthy approach to achieving your weight loss goals. A personalized intermittent fasting plan from an expert can make all the difference, especially when dealing with unique health circumstances.
Pre-existing Health Conditions
-
Diabetes (Type 1 or 2): If you have diabetes, especially if you’re on medication (like insulin), intermittent fasting can significantly impact your blood sugar levels. This requires careful monitoring and adjustment of medication under medical supervision to prevent hypoglycemia ( dangerously low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia.
-
Thyroid Disorders: Individuals with thyroid conditions, particularly hypothyroidism, should consult their doctor before starting intermittent fasting. Fasting can sometimes affect thyroid hormone production, and adjustments to medication or fasting protocols might be necessary.
-
Cardiovascular Disease: While intermittent fasting can benefit heart health for some, individuals with existing heart conditions should discuss it with their cardiologist.
-
Eating Disorders (Past or Present): If you have a history of disordered eating or an active eating disorder, intermittent fasting can potentially exacerbate these issues due to its restrictive nature. It’s highly advisable to work with a therapist or dietitian specializing in eating disorders.
Medications and Supplements
-
Regular Medications: If you’re taking any prescription medications, particularly those that need to be taken with food or at specific times, discuss your intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss with your doctor or pharmacist. Fasting can alter medication absorption and effectiveness.
-
Supplements: Certain supplements might be better absorbed with food, and some might need to be avoided during fasting windows.
Specific Life Stages
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Intermittent fasting is generally not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as these periods demand consistent nutrient intake for both mother and baby’s health and development.
-
Children and Adolescents: Growing bodies have high energy and nutrient demands. Intermittent fasting is not typically recommended for children or adolescents unless under strict medical supervision for specific therapeutic reasons.
-
Underweight or Frail Individuals: If you are already underweight or have a frail constitution, further restricting your eating window could be detrimental to your health.
If you fall into any of these categories, or if you simply feel unsure about how to start safely, consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or a registered dietitian. They can assess your individual health status, provide personalized recommendations for an intermittent fasting plan, and help you navigate any potential challenges, ensuring your journey to weight reduction is safe and effective. Don’t hesitate to seek expert advice; it’s an investment in your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I drink anything during my fasting window besides water? A1: Yes! During your fasting window, you can typically drink plain water, black coffee, and unsweetened tea. These beverages contain negligible calories and won’t break your fast. Some people also include sparkling water, and a tiny pinch of pink Himalayan salt in water can help with electrolytes. Avoid any drinks with sugar, milk, cream, or artificial sweeteners, as these can trigger an insulin response and negate the benefits of the fast.
Q2: Will intermittent fasting make me lose muscle mass? A2: Not necessarily. While some initial muscle breakdown can occur during fasting, studies show that intermittent fasting, especially when combined with adequate protein intake during your eating window and resistance training, is generally effective at preserving muscle mass while promoting fat loss. In fact, the increase in human growth hormone (HGH) during fasting can help protect lean muscle tissue. Focus on consuming sufficient protein in your feeding window to support muscle maintenance.
Q3: How long does it take to see results with an intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss? A3: The timeline for results varies greatly depending on your starting weight, consistency, and overall diet quality. Many people report initial weight loss (often water weight) within the first week or two. Sustainable fat loss typically becomes noticeable within 3-4 weeks. Remember that true transformation, which involves significant weight reduction and body composition changes, is a marathon, not a sprint. Consistency is far more important than extreme measures.
Q4: Is intermittent fasting safe for everyone? A4: While generally safe for healthy adults, intermittent fasting is not for everyone. It’s not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with a history of eating disorders, those who are underweight, or individuals with certain medical conditions like diabetes (especially if on medication) without medical supervision. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary regimen.
Q5: What should I eat after my fast? A5: When breaking your fast, prioritize nutrient-dense, whole foods. Focus on a balanced meal that includes lean protein (e.g., chicken, fish, eggs), healthy fats (e.g., avocado, nuts), and fiber-rich complex carbohydrates (e.g., vegetables, fruits, whole grains). Avoid highly processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of refined carbohydrates, as these can cause blood sugar spikes and digestive discomfort after a fasted state.
Conclusion
Embarking on an intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss is a journey that promises more than just a slimmer waistline. It’s an opportunity to reprogram your body for optimal fat metabolism, enhance mental clarity, and unlock a host of profound health benefits that extend far beyond the scale. We’ve seen that the key isn’t rigid adherence to a single protocol, but rather finding the intermittent fasting plan that harmonizes with your unique body, lifestyle, and goals. From understanding the underlying science of how it helps you burn fat and slim down, to exploring various schedules, and crucially, tailoring your approach based on individual needs like gender and age – the path to sustainable weight reduction is deeply personal.
Remember, the quality of your nutrition during your eating windows is paramount. Intermittent fasting empowers you to be more intentional about your food choices, turning your body into an efficient fat-burning machine. While challenges like hunger and low energy may arise, they are often temporary and manageable with smart strategies. And if you have any pre-existing health conditions or concerns, always consult a healthcare professional to ensure your journey is safe and effective.
So, are you ready to ditch the diet mentality and embrace a more intuitive, powerful way of eating? Start small, listen to your body, and adjust as you go. Your personalized intermittent fasting schedule for weight loss isn’t just about shedding pounds; it’s about building a healthier, more vibrant, and empowered version of yourself. What small step will you take today to begin crafting your ideal intermittent fasting journey?